Innovative Approaches to Managing Inoperable Brain Tumors
Brain tumors remain one of the most challenging medical conditions due to their complex nature and the impact they have on the central nervous system. Among these, the term inoperable brain tumor refers to tumors that cannot be surgically removed due to their size, location, or the patient's overall health. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of inoperable brain tumors, examining the latest treatment options, ongoing research, and holistic care strategies for patients.
Understanding Inoperable Brain Tumors
Brain tumors can be classified into two categories: primary tumors, which originate in the brain, and secondary tumors, which spread from other parts of the body. When a tumor is classified as inoperable, it means that surgical intervention is deemed too risky or impossible due to various factors:
- Location: Tumors positioned near critical areas of the brain, such as those controlling vital functions.
- Size: Large tumors may invade essential brain structures, making removal dangerous.
- Type: Certain tumors, like diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas (DIPG), are inherently difficult to remove.
- Patient’s Health: The overall health and comorbidities of the patient can also affect surgical eligibility.
Diagnostic Methods for Inoperable Brain Tumors
The journey to diagnosis is critical in managing inoperable brain tumors. Accurate diagnosis is achieved through a combination of imaging and biopsy techniques:
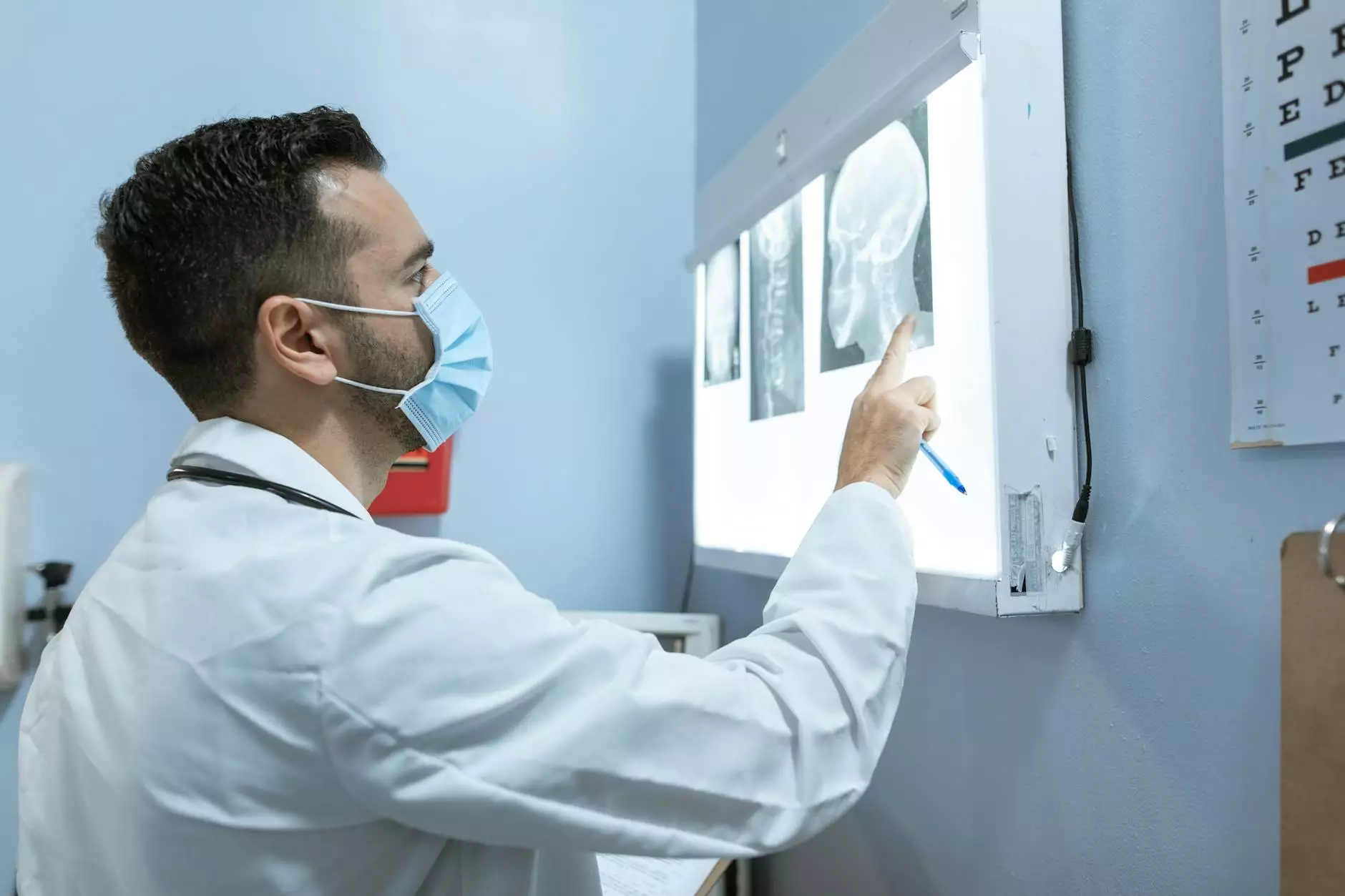
1. Imaging Techniques
Advanced imaging plays a crucial role in identifying and monitoring brain tumors:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): This is the primary tool due to its high-resolution images that help visualize the brain's structures.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: CT scans are often used for quick assessment, particularly in emergency scenarios.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET): PET scans can help evaluate tumor metabolism and differentiate between tumor types.
2. Biopsy Procedures
When necessary, a biopsy may be performed to obtain tissue samples for histological examination:
- Stereotactic Biopsy: A minimally invasive procedure guided by imaging allows for precise tissue sampling.
- Open Biopsy: Though riskier, this procedure provides a larger tissue sample if less invasive methods are inconclusive.
Treatment Options for Inoperable Brain Tumors
While surgery may not be an option, patients diagnosed with inoperable brain tumors have various treatment alternatives that can enhance quality of life and prolong survival:
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy utilizes drugs to target and kill cancer cells. This approach may vary based on the type of tumor and its genetic makeup:
- Systemic Chemotherapy: Administering drugs that circulate throughout the body.
- Targeted Therapy: Medications designed to target specific characteristics of cancer cells.
- Clinical Trials: Patients may explore clinical trials offering emerging therapies tailored to specific tumor types.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to reduce tumor size or limit growth:
- Conventional Radiation Therapy: Aimed at precisely targeting the tumor while minimizing exposure to healthy tissue.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery: A non-invasive procedure delivering targeted radiation in high doses to precisely destroy tumor cells over a few sessions.
Supportive and Palliative Care
For patients with inoperable brain tumors, supportive therapies focus on maintaining quality of life:
- Pain Management: Effective management of pain through medications and therapies to enhance comfort.
- Physical Therapy: Strategies to improve mobility and overcome challenges posed by the tumor's effects.
- Psychosocial Support: Counseling services to assist patients and families in coping with the emotional aspects of a brain tumor diagnosis.
Emerging Research and Future Perspectives
The field of oncology continuously evolves, with numerous studies focused on inoperable brain tumors. Innovations include:
- Immunotherapy: Leveraging the body's immune system to target and fight cancer cells.
- Gene Therapy: Targeting genetic mutations responsible for tumor growth.
- Nanotechnology: Utilizing nanoparticles to improve drug delivery and minimize side effects.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities associated with inoperable brain tumors can be daunting for patients and their families. However, advancements in treatment strategies, ongoing research, and comprehensive support systems offer hope and improved outcomes. Understanding the available options and connecting with healthcare professionals at reputable medical centers like MediGlobus can empower patients to make informed decisions in their battle against this formidable opponent. By staying abreast of the latest developments and embracing a multi-disciplinary approach, patients can optimize their health and well-being.
Getting Help at MediGlobus
At MediGlobus, we understand the unique challenges faced by those dealing with inoperable brain tumors. Our team is dedicated to providing:
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Tailored to each patient's specific needs and tumor characteristics.
- Access to Leading Specialists: Collaborating with top medical professionals in oncology and neurology.
- Continued Care and Monitoring: Ongoing assessments to adapt treatment as necessary and ensure the best possible outcomes.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can assist you or a loved one dealing with an inoperable brain tumor.